Maximum Seller Concessions:
- Seller concessions are the amount of closing costs, property taxes, and insurance paid by the seller when a home is sold.
- The maximum seller concessions allowable when a home buyer is getting a mortgage determine the limit of assistance the seller can provide.
Importance of Seller Concessions:
- Seller concessions can help buyers with upfront costs and make the purchase of a home more feasible.
- Understanding the limits on seller concessions is crucial for both buyers and sellers in a real estate transaction.
Types of Seller Concessions:
- Common types of seller concessions include the seller paying for the buyer's closing costs, pre-paid interest, and property taxes.
- Negotiating seller concessions can be an important aspect of the home buying process.
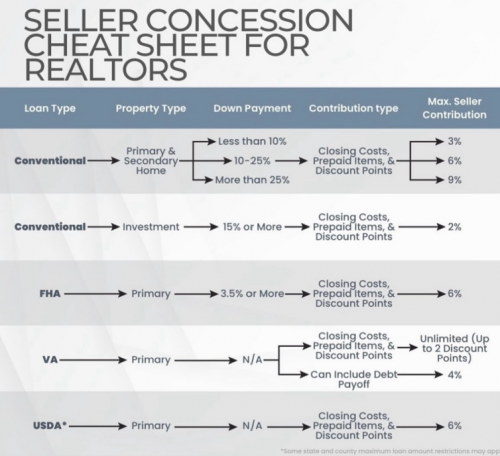
Seller Concessions Limitations:
- The limit on seller concessions can vary depending on the type of mortgage and the buyer's down payment.
- Buyers should be aware of these limitations when negotiating a real estate transaction.
Effect on Mortgage Terms:
- Excessive seller concessions can affect the terms of the buyer's mortgage and may lead to complications in the loan approval process.
- Both buyers and sellers should carefully consider the impact of concessions on the overall transaction.
Regulations and Guidance:
- Regulations and guidance from government agencies such as the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide specific rules on seller concessions.
- Compliance with these regulations is essential for a successful and legally sound real estate transaction.
Professional Consultation:
- Seeking advice from a qualified real estate agent or mortgage professional can help both buyers and sellers understand the implications of seller concessions.
- Professional guidance can ensure that seller concessions are utilized effectively and in accordance with applicable regulations.
Seller concessions, also known as Interested Party Contributions (IPCs), can be used for:

- **Payments or credits related to acquiring the property**, such as:
- Origination fees
- Discount points
- Commitment fees
- Appraisal costs
- Transfer taxes
- Stamps
- Attorneys’ fees
- Survey charges
- Title insurance premiums or charges
- Real estate tax service fees
- Funds to subsidize a temporary or permanent interest rate buydown
- Prepaid items like interest charges, real estate taxes, property insurance premiums, homeowners’ association (HOA) assessments, initial and/or renewal mortgage insurance premiums, and escrow accruals for mortgage insurance coverage
- **Typical fees and/or closing costs paid by a seller in accordance with local custom**, known as common and customary fees or costs, which are not subject to Fannie Mae IPC limits.

Seller concessions cannot be used for:
- Making the borrower’s down payment
- Meeting financial reserve requirements
- Meeting minimum borrower contribution requirements
Additionally, any concessions that exceed Fannie Mae IPC limits are considered sales concessions and must be deducted from the sales price when calculating Loan-to-Value (LTV) and Combined Loan-to-Value (CLTV) ratios for underwriting and eligibility purposes.
Source: Guidelines context provided, specifically the sections "Financing concessions" and "IPC Limits" under "Lender Checklist for IPCs".

Christopher Gibson
NMLS #1910430 | C2 Financial Corp NMLS #135622
Call me: 720-449-6622
Email me: C@ChrisRayGibson.com